网管经验谈:将Ping命令功能发挥到最大
一个个路由才到达对方的,但到底是经过了哪些路由呢?通过此参数就可以设定你想探测经过的路由的个数,不过限制在了9个,也就是说你只能跟踪到9个路由,如果想探测更多,可以通过其他命令实现,我将在以后的文章中给大家讲解。以下为示例:
C:\>ping -n 1 -r 9 202.96.105.101 (发送一个数据包,最多记录9个路由)
Pinging 202.96.105.101 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 202.96.105.101: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=249
Route: 202.107.208.187 ->
202.107.210.214 ->
61.153.112.70 ->
61.153.112.89 ->
202.96.105.149 ->
202.96.105.97 ->
202.96.105.101 ->
202.96.105.150 ->
61.153.112.90
Ping statistics for 202.96.105.101:
Packets: Sent = 1, Received = 1, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 10ms, Maximum = 10ms, Average = 10ms
从上面我就可以知道从我的计算机到202.96.105.101一共通过了202.107.208.187 ,202.107.210.214 , 61.153.112.70 , 61.153.112.89 , 202.96.105.149 , 202.96.105.97这几个路由。
-s count Timestamp for count hops.
指定 count 指定的跃点数的时间戳。
此参数和-r差不多,只是这个参数不记录数据包返回所经过的路由,最多也只记录4个。
-j host-list Loose source route along host-list.
利用 computer-list 指定的计算机列表路由数据包。连续

C:\>ping -n 1 -r 9 202.96.105.101 (发送一个数据包,最多记录9个路由)
Pinging 202.96.105.101 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 202.96.105.101: bytes=32 time=10ms TTL=249
Route: 202.107.208.187 ->
202.107.210.214 ->
61.153.112.70 ->
61.153.112.89 ->
202.96.105.149 ->
202.96.105.97 ->
202.96.105.101 ->
202.96.105.150 ->
61.153.112.90
Ping statistics for 202.96.105.101:
Packets: Sent = 1, Received = 1, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 10ms, Maximum = 10ms, Average = 10ms
从上面我就可以知道从我的计算机到202.96.105.101一共通过了202.107.208.187 ,202.107.210.214 , 61.153.112.70 , 61.153.112.89 , 202.96.105.149 , 202.96.105.97这几个路由。
-s count Timestamp for count hops.
指定 count 指定的跃点数的时间戳。
此参数和-r差不多,只是这个参数不记录数据包返回所经过的路由,最多也只记录4个。
-j host-list Loose source route along host-list.
利用 computer-list 指定的计算机列表路由数据包。连续




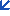 天下网吧·网吧天下
天下网吧·网吧天下